Chat Targeting - Configuring the Triggers
Triggers control the display of the chat and allow targeting the visitors based on their behavior on the website. Associated with conditions on Custom Variables, the targeting may be quite evolved and be the translation of some business rules.
Trigger
You define a meaningful label for the trigger. Note that the agent will see which trigger is the source of the conversation, information given by the label.
You can activate / deactivate a trigger when needed.
You can have a trigger with no condition. This means that it will always try to execute. This is useful for the click to chat use case, for placing a button somewhere in the website.
Note that for when the trigger is marked as “Execute only if agents are available”, the conditions configured in the trigger are only the first step of the decision process to execute the actions or not; the second step being evaluation by the server and depends on the presence and occupancy of the agents. Meaning that even if the trigger has no condition, the actions won’t be executed if no agents are present, for example.
Queuing
The Queuing factor field, empty by default, controls the extra slots that are allowed in the waiting queue for this trigger. When empty, it uses the value configured in the RingCX Messaging source.
Conditions
You can define a set of conditions for the trigger.
Each condition is defined by selecting what matches what values, and when.
What
The Chat Manager tracks the predefined criteria:
| Criterion | Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chat opened | Boolean | true | Corresponds to whether the chat window is opened (true) or minimized (false). |
| Chat shown | Boolean | false | Corresponds to whether or not the chat window is displayed. |
| Day of week | Special | Monday | |
| Time | Special | 17:45 | |
| Identity | Boolean | true | Corresponds to whether an identity has been set. |
| Page path | String | /shop/product.php?id=58 | Corresponds to the strict path of the page URL i.e. without the scheme, the domain and the anchor, and starting with a slash. |
| Page URL | String | https://www.myshop.com/shop/product.php?id=58#bottom | The full page URL, scheme and anchor included. You may prefer using the “Page path” as it allows using a nicer “Starts with” (that can match a full website section if URL are well thought, e.g. “Starts with” “/dresses/” will match “/dresses/” and “/dresses/587-pink-dress”). |
| Page title | String | Pink Dress - My Shop | |
| Page visit count | Number | 2 | Corresponds to the number of pages viewed during the current visit. |
| Page visit duration (in seconds) | Number | 15 | |
| Signed identity (JWT) | Boolean | false | Corresponds to whether an identity signed with JWT has been set. If this is true, the “Identity” is also true. |
| Visit count | Number | 1 | |
| Visit duration (in seconds) | Number | 45 |
Other predefined criteria may be added in the future.
You may also use any of the configured custom variables.
When
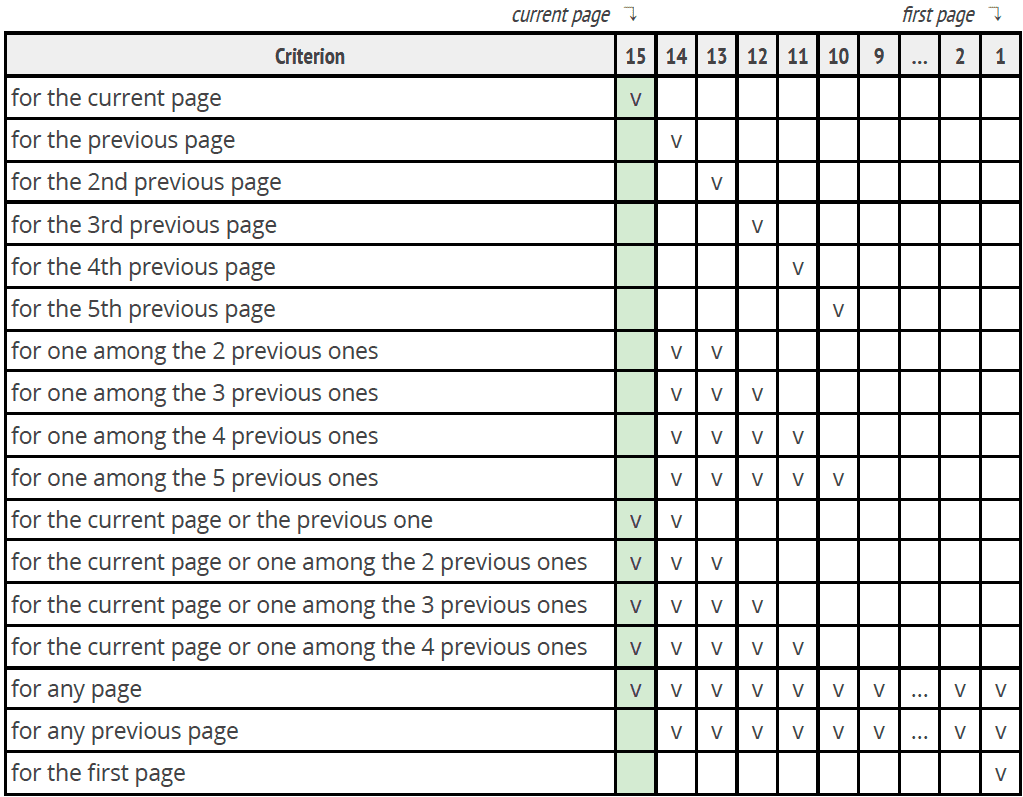
As the Chat Manager uses a historical store, you define when the condition must have matched. The default is “for the current page”. Among the historical positions available, the most useful are:
- for the current page
- for the previous page
- for any page
- for any previous page
Here is an example that specifies the meaning of each of the historical positions. The visitor has seen 15 pages, the current page is the 15th:
Value
Each criterion is matched against a value, with an operator. The operators depend on the type of the criterion.
Common Operators
The operator “is” is the equality matcher.
The operator “is present” matches for when a criterion is defined (i.e. found) and is not blank. The Chat Manager may find the string (e.g. the value of a form field), but it can be blank (e.g. not filled yet). It has the same meaning as in RingCX Digital Communities for the validation of presence of the title of Questions for example. For Boolean, it has the meaning of is defined and is true.
The operator “is not present” is its opposite, and target values that are blank or that can’t be found. You may notice the utility: if the condition is is not “” (i.e. is not an empty string), if the Chat Manager can’t find it (i.e. it is seen as not defined), then, the condition is true, as it is not defined, it is not an empty string. The operator “is not present” is helpful in many of those cases. For Boolean, it has the meaning of is not defined or is false.
Number Type
Number typed criterion have the extra *“is greater or equal to” (criterion ≥ N) and “is lesser or equal to” (criterion ≤ N).
String Type
String- type criterion has the extra “is not”, “contains”, “doesn’t contain”, “starts with” and “ends with”.
In addition, multiple values can be set for the same string-type criterion, using a comma-separated list.
List with multiple values behave as follow:
- For positive conditions (“is”, “contains”, “starts_with”, “ends_withs”), the result is true if ANY of the list values match the source value.
- For negative conditions (“is not”, “does not contain”), the result is true if NONE of the list values match the source value.
String comparison happens after a normalization step. For example, the string “ La Naïveté ”, that contains many extra spaces, accented letters and uppercase, is normalized into “la naivete” and is strictly equivalent to it in terms of comparison.
Example of matching:
| Source | Normed Source | Operator | Value | Normed Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is | “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is | “la naivete” | “la naivete” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is | “ la naivete ” | “la naivete” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is | “la naivete, hello” | “la naivete, des gens” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is not | “la naivete” | “la naivete” | false |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | is not | “la naivete, des gens” | “la naivete, des gens” | false |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | contains | “naïve” | “naive” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | contains | “ naïve ” | “naive” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | starts with | “ La ” | “la” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | starts with | “la” | “la” | true |
| “ La Naïveté des Gens ” | “la naivete des gens” | ends with | “ des gens ” | “des gens” | true |
| “ La Naïveté ” | “la naivete” | contains | “naif” | “naif” | false |
Boolean Type
There are no dedicated operators.
Values for Day of Week
These are predefined: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
Matching can be exact, but you may use the “is greater/lesser or equal to” to match a range of days. For example “is greater or equal to Saturday” will match the whole weekend. And “is lesser or equal to Friday” will match days from Monday to Friday.
Values for Time
These are predefined: from 00:00 to 23:45, with 15 minutes interval. It corresponds to the universal notation of time. E.g. half past midnight, noted 00:30.
You can use the “is greater or equal to” and/or “is lesser or equal to” to match a range of times.
For example:
- “is greater or equal to 20:00” will match the whole evening, from 20:00 to 23:59:59.
- combining “is greater or equal to 07:15” and “is lesser or equal to 19:45” will match the whole day from 07:15 to 19:45.
Combining Conditions
You may have several conditions for one trigger. They combine with a logical “and”, meaning that each of the conditions must match for the trigger to be activated.
To handle the logical “or” case, you have to create several triggers.
Examples of Evolved Conditions
By combining conditions and by leveraging the historical positions, you may create interesting scenarios.
You can target visitors leaving a funnel: “Page URL”, for the previous page, contains “/my-cart/order/” AND “Page URL”, for the current page, doesn’t contain “/my-cart/order/”.
You can target visitors clearing their cart: “Custom - Cart number of products”, for any page, is greater or equal to “1” AND “Custom - Cart number of products”, for the current page, is “0”.
Actions
At least one action is required for a trigger.
Direct Chat Window Display
The action Show the chat minimized will launch the chat and display the chat window in its minimized state.
The action Show and open the chat will launch the chat and display the chat window in its minimized state and transition it nicely to its opened state.
The actions are idempotent. If several Triggers execute a Show and open the chat, only the first one will actually launch the chat and open the chat window. In the same way, if a first trigger does Show the chat minimized, a second that wants to Show and open the chat will just open the chat window, as it is already launched.
Catalog Item Display
For each of these actions, you have to choose from the catalog the corresponding item you want to be shown.
Automatic Message
You may display to the visitor a message appearing when the chat client is launched. A standard notification is also fired.
Choose one message from the catalog.
Note that you can’t have this action on its own. For the case when you want to display an automatic message in the middle of a conversation, you have to select at least the Show and open the chat action (as when already launched and shown, it will be a no-op).
When combined with the action of showing a button or an invitation, the automatic message is shown when the chat window is shown, i.e. after the visitor clicks on the “action” of the selected item.
Moreover, if an automatic message has already been sent, a second one with the same text won’t be sent. There is a unicity on the automatic message text.
Hide Other Elements
You may want to hide the already displayed items (buttons & invitations) when the trigger is activated.
Note that this will hide every item already displayed, even fixed buttons.
Post Activation Behavior
You may define the behavior of the chat manager after a trigger execution.
The option No other trigger is activated after this one means that if this trigger is executed, no other trigger can be executed afterward, even after a page reload.
The option This trigger is activated only once per visit means that the trigger will be executed only once per visit. Useful when displaying an invitation pop-up.
Processing
In addition to actions, there can be processings associated with the trigger for when a conversation starts.
Categorization
You may define some categories associated with the trigger. Each conversation started from this trigger will be categorized accordingly.
Language
You may define the language associated with the trigger. Each message of the conversation started from this trigger will have its language set accordingly.
This also sets the locale of the chat client for the visitor.